Ultrasound-guided interventions
Technology is bringing more and more facilities to our daily lives. In the field of medicine, ultrasound-guided procedures ensure that some diagnostic & therapeutic procedures can be performed with minimal invasion of the body.
Created in the First World War to detect objects at the bottom of the sea, ultrasound only arrived in medicine in the 1940s, when it revolutionized diagnostic procedures – even with the patient having to be submerged in a bathtub and the quality of the images being very low.
Nowadays, the quality of images has reached levels of extreme quality, and allow procedures guided by ultrasound to reach a level of excellence.
ULTRASOUND-GUIDED PROCEDURES
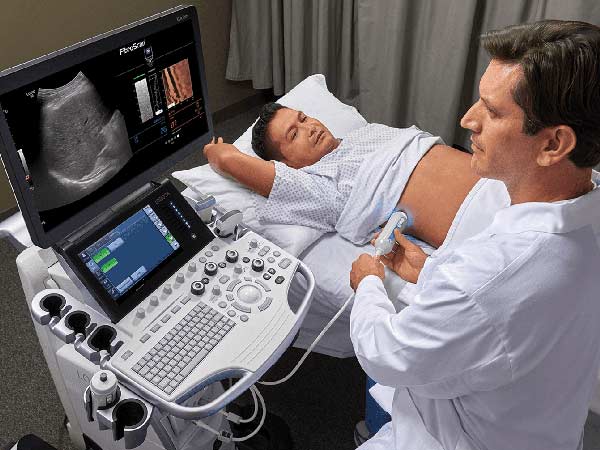
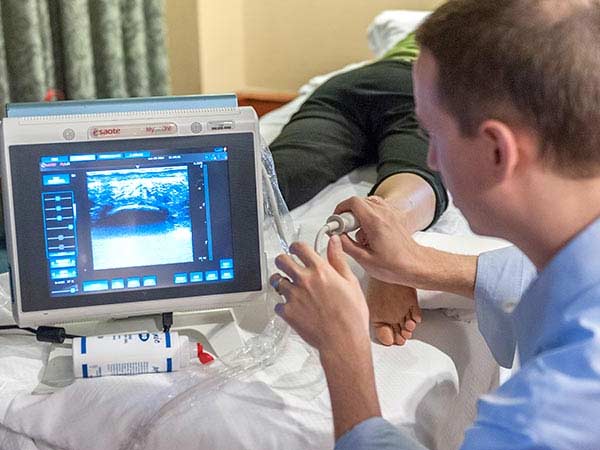
Among interventional medicine, ultrasound has also served to guide physicians in minimally invasive procedures. Through the images, it is possible to have more precision of the place where it is necessary to carry out interventions, such as knowing the exact place & path where it is necessary to insert a needle. Hence, a variety of Interventional Ultrasound guided procedures can be performed which can include the following:.
- Ultrasound guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC)– using a thin sterile metallic needle placed after local infiltration of anaesthetic agent. Needle targetted to nodule/mass/abnormality visualised on focussed ultrasound. Most useful for relatively vascular organs like Thyroid & targets like small lymphnodes where biopsy may have risk of complications & less likely yield.

- Ultrasound guided Truecut (Core) biopsy– usually performed using a co-axial biopsy gun introduced after local infiltration of anaesthetic agent. Biopsy gun targetted to nodule/mass/lymphnode/other abnormality localised on focussed ultrasound. Such biopsies can be performed for abnormalities in various body regions accessible by ultrasound eg. Neck, axilla, breast, abdominal cavity, prostate & musculoskeletal structures etc.

- Ultrasound guided Aspiration/single time drainage – procedure similar to FNAC, used for aspiration of thin or thick fluid collections in various body regions eg. Pleural fluid (fluid in chest cavity), ascites (fluid in abdominal cavity), abscesses (in any accessible body region eg. Breast, liver etc). The material aspirated can be subjected to various laboratory investigations eg. Culture & sensitivity assessment

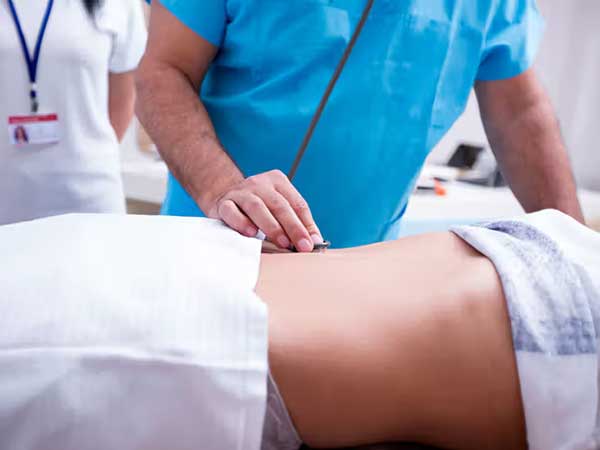
- Ultrasound guided Drainage Catheter placement- performed in case of relatively large volume or thick collections. A tube (catheter) is deployed into the fluid collection through a short surgical process that is carried out under ultrasound guidance. Catheter is secured with help of sutures to help it maintain its position & connected to a urobag to collect the draining contents. The catheter needs to be retained till the output sufficiently decreases & there is clinical improvement. Collections in various body regions eg. Multiseptate pleural effusion, liver abscess, recurrent ascites refractory to medical management & post operative seromas can be managed by this method.


Catheter placed in abdominal cavity under USG guidance
Besides above procedures which can be performed for various body regions, following are some of the USG guided interventional procedures which can be performed for the musculoskeletal system:
- Peripheral nerve blocks: for pain relief
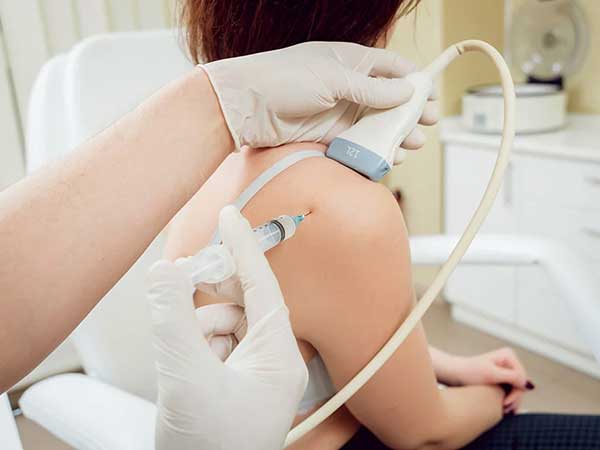
- Joint injections – for inflammatory arthritis/ osteoarthritis of various joints
- Hydrodissection For Carpal tunnel syndrome
- PRP (platelet-rich plasma) injection: at sites of muscle/ligament/tendon tear to achieve gradual healing of the tear
- Trigger point injection
General instructions for USG guided procedures
– Doctor needs details of your comorbidities if any eg. Hypertension, Drug allergies etc. prior to procedure
– Mention about any medication that you are taking eg. Blood thinners. Some medications like blood thinners increase risk of bleeding during & post procedure. They may need to be omitted for a sufficient time to reduce the risk of bleeding.
– Please mention details of any previous surgical/angiographic procedures that you have undergone prior to this procedure and if any complications eg. Excessive bleeding that may have occurred.
-Always come accompanied by an attendant when coming for a guided procedure