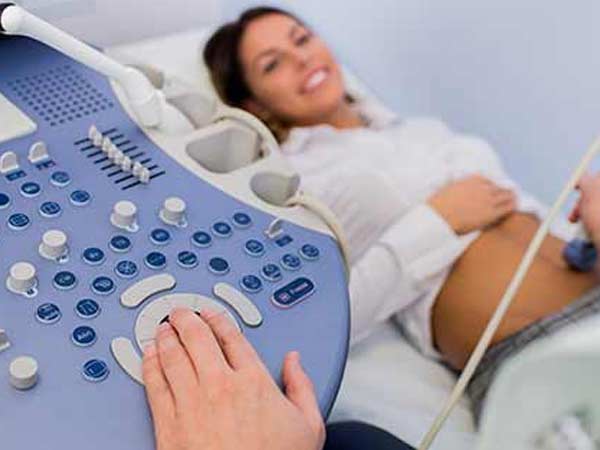
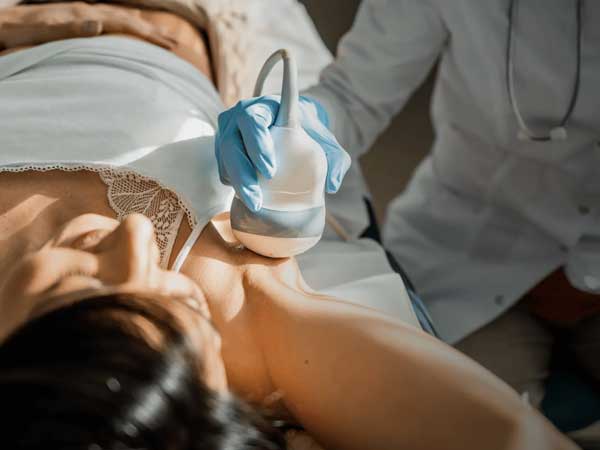
Gynecological ultrasound examines the female genital tract including uterus, cervix, ovaries & fallopian tubes.
What are the types of gynecological ultrasound?
Gynaecologic ultrasounds can be distinguished based on the route of performing ultrasound:
- Trans-abdominal ultrasound: allows examination of the entire lower abdomen through the anterior abdominal wall & provides a wide view of the pelvic organs. It preferrably needs a well distended urinary bladder.
– pre-requisite: Patient to drink water & retain urine
– preparation: No bowel preparation needed.
– Patient need not be empty stomach.
- Transvaginal or endovaginal ultrasound
Relevance of transvaginal ultrasound: While trans-abdominal ultrasound provides a global view of the female genital tract, transvaginal sonography (TVS) helps visualise the same areas but allows a more focussed assesment. It reaches the area of interest upclose via being placed in the vagina.
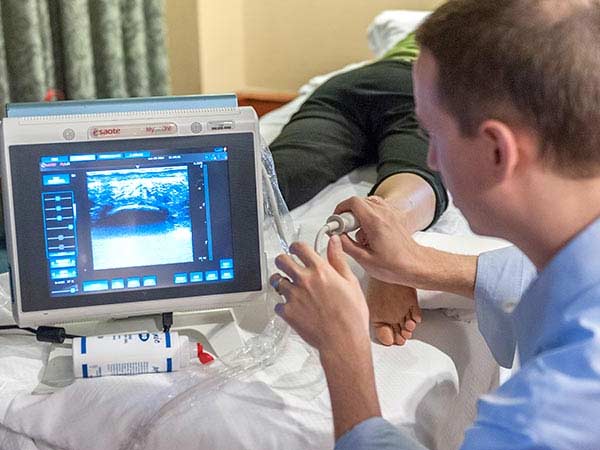
Procedure for TVS: the patient lies on a ultrasound couch and has a pillow under her pelvis to allow for probe maneuverability. The sonologist uses a transducer with gel. The probe, that is, the transducer, is protected by a condom and introduced into the vaginal canal. If the patient has a latex allergy, she should alert the doctor in advance.
Generally, endovaginal ultrasound is used as a routine exam, and can be requested in visits to the gynecologist, or as a way to identify the causes of problems and symptoms such as:
- abnormal bleeding, with no apparent cause;
- before and after IUD insertion ;
- the suspected presence of cyst;
- suspected ectopic pregnancy;
- suspected infertility ;
- pelvic pain.
In addition, the test can also be recommended during pregnancy, as it is considered a safe procedure.
Example case:
Young lady presenting with recurrent mid cycle vaginal bleeding, advised transvaginal USG
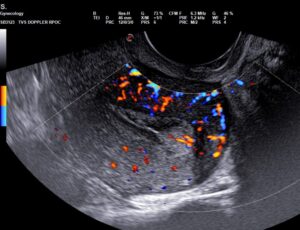
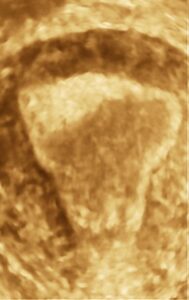
What is the importance of gynecological ultrasound for women’s health?
Gynecological ultrasounds are among the most commonly performed sonographic examinations requested for women. Used as preventive measures, they contribute to the early identification of diseases and allow the treatment to start quickly, increasing the chances of cure and simplifying treatment.